
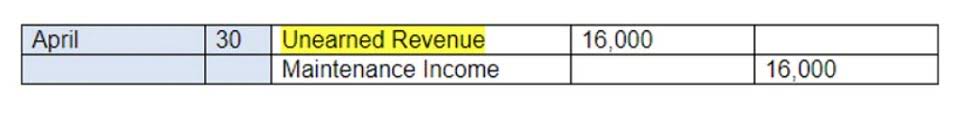
It is deferred to the next accounting period by crediting a liability account such as Unearned Revenues. Next period (when it is earned) a journal entry will be made to debit the liability account and to credit a revenue account. The first transaction that Joe will record for his corporation is his personal investment of $20,000 in exchange for 5,000 shares of Direct Delivery’s common stock.
Understanding Financial Statements

The income statement reports the revenues, gains, expenses, losses, net income and other totals for the period of time shown in the heading https://www.bookstime.com/articles/accounting-san-diego of the statement. If a company’s stock is publicly traded, earnings per share must appear on the face of the income statement. Accrual basis accounting is a method in which transactions are recorded when they occur, regardless of when cash is received or paid. In this method, revenues and expenses are recognized when they are earned or incurred, respectively.
Key Accounting Principles

Other expenses to be matched with December’s revenues would be such things as gas for the delivery van and advertising spots on the radio. This explanation of accounting basics will introduce you to some basic accounting principles, accounting concepts, and accounting terminology. Once you become familiar with some of these terms and concepts, you will feel comfortable navigating through the explanations, quizzes, quick tests, video training, and other features on AccountingCoach.com.
- Conservatism says that the entity has to provide for any expected losses or expenses; however, it does not recognize future revenue expected.
- For example, if Joe delivers 1,000 parcels in December for $4 per delivery, he has technically earned fees totaling $4,000 for that month.
- Entity Accounts are kept for entities and not the people who own or run the company.
- They help to provide a framework for understanding and interpreting financial information.
- The financial statements are meant to convey the financial position of the company and not to persuade end users to take certain actions.
A Story for Relating to Accounting Basics
- Accounting’s accrual principle demands that financial accounts represent transactions as they occur, not necessarily when cash changes hands.
- The cash basis of accounting is usually followed by individuals and small companies, but is not in compliance with accounting’s matching principle.
- While often used interchangeably, bookkeeping and accounting serve distinct purposes.
- However, businesses should recognize expenses sooner, when there’s even a reasonable possibility that they will be incurred.
The owner’s interest is the value of total assets left after all liabilities to creditors and lenders are settled. It is decreased by withdrawals by owners (dividends in corporations) and expenses. Theoretically, there are a number of bases that could be used to derive the value at which transactions are recorded. However, historical cost is the only one of these that needs to be considered in the context of FA2.
- This approach also requires estimates and judgments, such as determining the allowance for doubtful accounts, which impacts financial statement accuracy.
- Historical Cost Principle – requires companies to record the purchase of goods, services, or capital assets at the price they paid for them.
- Next period (when it is earned) a journal entry will be made to debit the liability account and to credit a revenue account.
- Examples include historical cost, revenue recognition, full disclosure, materiality, and consistency.
- What it means is that for a business, an account book can record only those transactions which involve monetary transfers.
This means that estimates need to be made when preparing financial statements. Prudence requires that, whenever such uncertainty exists, preparers retained earnings of financial statements take a careful approach to the figures and information that they include in the financial statements. It’s the process of recording, classifying, summarizing, analyzing, and interpreting financial transactions. Materiality Concept – anything that would change a financial statement user’s mind or decision about the company should be recorded or noted in the financial statements. If a business event occurred that is so insignificant that an investor or creditor wouldn’t care about it, the event need not be recorded.
- It is the amount invested by the owner in the business in the form of cash or any other kind of asset.
- Of course, the accountant or auditor is free to come to a different conclusion if there’s evidence that the business can’t pay back its loan or meet other obligations.
- Understanding these financial statements is crucial for making informed decisions about a company’s financial health.
- Let us understand the objectives of financial accounting concepts through the explanation below.
- As a result of this principle, a company’s financial statements will include many disclosures and schedules in the notes to the financial statements.
The High Cost of Neglecting Essential Finance Metrics for Your Business
When a cause-and-effect relationship isn’t clear, expenses are reported in the accounting period when the cost is used up. For example, the $120,000 cost of equipment with a 10-year life will be charged to expense at a rate of $1,000 per month. The going concern assumption means the accountant believes that the company will not be liquidated in the foreseeable future. In other words, the company will be able to continue operating long enough to meet its obligations and commitments.

As a result these items are not reported among the assets appearing on the balance sheet. If a company does not pay cash right away for an expense or fundamental accounting concepts for an asset, you cannot credit Cash. Because the company owes someone the money for its purchase, we say it has an obligation or liability to pay. The most likely liability account involved in business obligations is Accounts Payable.
